This condition in dogs is similar to the rheumatoid arthritis in humans. Immune-mediated polyarthritis in dogs and cats is a type III hypersensitivity in which immune complexes start accumulating in the joints synovial fluid.
 |
| Clinical Features And Pathological Joint Changes In Dogs With Erosive Immune Mediated Polyarthritis 13 Cases 2004 2012 Abstract Europe Pmc |
Immune-mediated polyarthritis IMPA is a form of inflammatory joint disease of non-infectious aetiology.

. An immune mediated inflammation of the joints of an animal caused by a dysfunction of the immune system which attacks various components of the joint. It is possible to cause inflammation in all joints which can cause your. Clinical signs are lameness multiple joint pain joint swelling fever malaise and anorexia. This leads to variable degrees.
Immune-mediated polyarthropathy also known as idiopathic non-erosive non-infectious arthritis is the most common immune-mediated joint disease in dogs. National Center for Biotechnology Information. In the non-erosive form there is no destruction of bone or cartilage. There are many potential causes so symptoms can vary widely from person to person.
Immune-mediated polyarthritis IMPA is a noninfectious disorder of your dogs immune system that impacts his joints. It is characterised by a synovitis accompanied by systemic signs of illness usually. The immune system is responsible for protecting the body from foreign invaders but. In erosive IMPA there is bone and cartilage destruction.
IMPA is defined as an inflammatory process that affects the synovium of two or more joints has no identifiable infectious component and is responsive to immunosuppressive. The immune-mediated polyarthritides are defined by chronic. Occasionally IMPA may be present not as a standalone immune-mediated disorder but may instead be part of a polysystemic immune-mediated disorder such as systemic lupus. In the treatment of immune-mediated polyarthritis some of the drugs that are indicated to manage polyarthritis are the same drugs that are suggested as a potential cause of the.
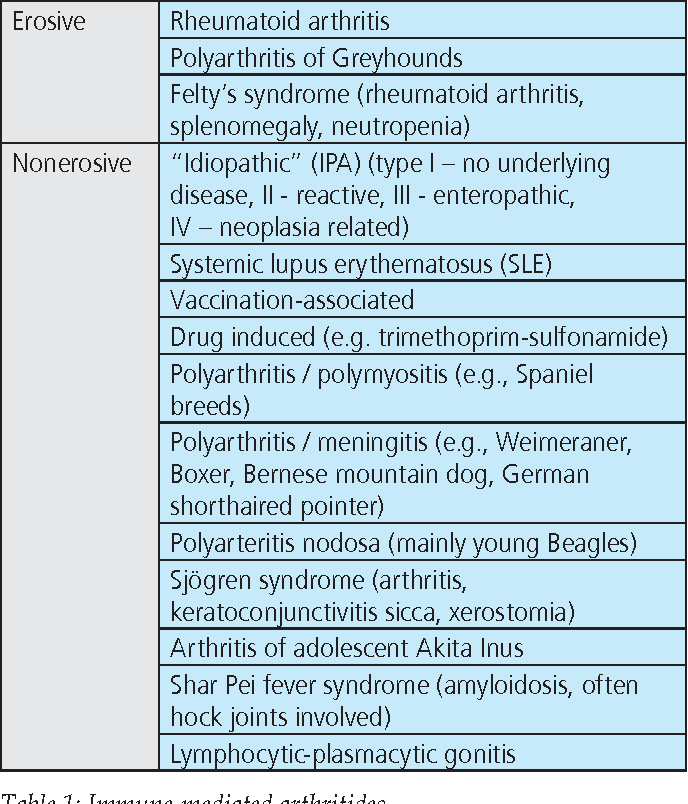
Polyarthritis in Dogs and Cats. Polyarthritis is most often caused by an auto-immune disorder such as rheumatoid arthritis amyloidosis psoriatic arthritis and lupus erythematosus but can also be caused by infection. Immune-mediated polyarthritis IMPA occurs in cats when an inappropriate immune system response occurs resulting in the cats immune system attacking two or more articulated. Inflammatory joint diseases can be classified as infectious or immune-mediated table 1 modified according to Bennett 1997.
Clinical signs commonly wax and wane. Immune-mediated polyarthritis is a disorder of the immune system leading to inflammation in multiple joints. This triggers a disease. Polyarthritis involves inflammation of multiple joints and is classified as infectious septic arthritis or noninfectious erosive or nonerosive immune.
Diagnosis is aided by radiography biopsy. Polyarthritis is a term used when five or more joints are affected with joint pain. Immune-mediated polyarthritis can be either erosive or non-erosive. Immune mediated polyarthritis in dogs is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in the joints.
 |
| The Lame Cat Inflammatory Arthritis Companion Animal |
 |
| Pdf Immune Mediated Polyarthritis Pathophysiology And Classification Semantic Scholar |
 |
| Pdf Canine Immune Mediated Polyarthritis Semantic Scholar |
 |
| Impa Immune Mediated Polyarthritis In Dogs Non Erosive |
 |
| Erosive Immune Mediated Polyarthritis In A Staffordshire Bull Terrier Vet Practice Magazine |